
⦁ The frontal process arises from the zygomatic bone’s top edge. Each process forms an important structural component of the skull. The zygomatic bone on each side is diamond-shaped with three processes that articulate with the frontal, temporal, and maxillary bones. The former carries the zygomaticofacial nerve and vessels, whilst the latter carries the zygomaticotemporal nerve and vessels. This canal divides into the zygomaticofacial and zygomaticotemporal canals, which open on the respective zygomatic bone surfaces. It has the zygomatico-orbital foramen, which is a portal to the bony canal located within the zygomatic bone. It constitutes the anterolateral region of the floor and the anterior part of the lateral wall and confronts the orbit. ⦁ The orbital surface is concave and smooth.

The zygomaticotemporal foramen, located near the base of the frontal process, transports the zygomaticotemporal nerve from the orbit to the temporal fossa. The posteromedial surface extends over the medial side of the temporal process, forming a portion of the infrate temporal fossa’s lateral wall. ⦁ The temporal (posteromedial) surface is concave with a rough triangular area medially for articulation with the maxilla and a smooth concave surface laterally that forms the anterior boundary of the temporal fossa and the lower part of the infrate temporal fossa. The lateral surface also acts as an attachment point for the zygomaticus major and zygomaticus minor muscles on the anterior half and the zygomaticus minor muscle on the posterior half. The zygomaticofacial nerve, artery, and vein pass via this foramen between the orbit and the face. It is smooth and convex, with a tiny aperture known as the zygomaticofacial foramen. ⦁ The malar (facial or cheekbone) surface is exposed to the elements. There are three surfaces to the zygomatic bone: malar, posteromedial, and orbital.
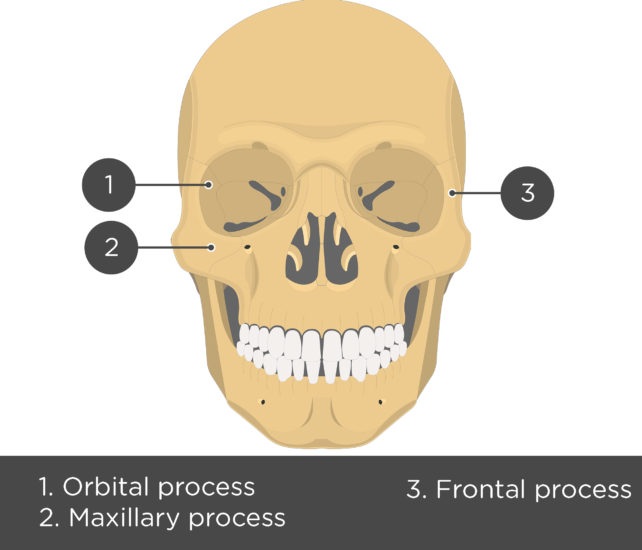
It provides stability and support to the midface and protection to the orbit. Besides its aesthetic significance, the zygomatic-maxillary region plays an important functional role. The zygomatic arch provides width to a person’s face and figures prominently in the oblique facial profile. The zygomatic bone is responsible for the malar prominence, an important aesthetic landmark in facial architecture. Inferiorly, it connects to the alveolus of the maxilla. Posteriorly, it forms the anterior portion of the zygomatic arch. Medially, it forms the lateral portion of the infraorbital rim. The superior projection connects with the frontal bone. The zygomatic bone has four projections, which give it the characteristic quadrilateral (diamond) shape. It borders the frontal bone lateral to the orbit and the sphenoid and maxilla medially.Īnatomical Structure of the Zygomatic Bone The term “zygomatic” comes from the Greek word “zygoma” which means “yoke.” The zygomatic bone on each side is located below and lateral to the eye socket. The zygomatic bones (also referred to as the malar bones) are a pair of quadrilateral-shaped bones responsible for the prominence of the cheeks.

The facial bones form the structure of the face. The bones of the skull can be categorized into the cranium and the face (see our article on radiographic positioning of the skull for the major projections used to image the cranial bones). The skull is made of several bones that are held together at sutures by connective tissue called sutural ligaments. Radiographic confirmation of zygomatic arch fractures allows early stabilization with better anatomic function and cosmetic results. Most zygomatic fractures are followed by a sensory abnormality, either hypoesthesia or anesthesia, in one or more branches of the infraorbital nerve.

In fact, the zygomatic arch is one of the most commonly fractured facial bones, typically following altercations in which the patient is punched in the face. Fractures of the zygoma region can occur with head trauma. The zygomatic arch (cheekbone) is composed of the temporal bone’s zygomatic process and the zygomatic bone’s temporal process, which is joined by an oblique suture, namely zygomaticotemporal suture.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
